Researchers from Osaka University and Japanese printing technologies supplier Toppan have productively developed cultured Wagyu beef employing a novel tissue modeling technology based mostly on 3D printing.
The engineering enabled the researchers to replicate the complicated tissue structures of Wagyu beef, together with muscle, excess fat and blood vessel tissue, in order to obtain the meat’s one of a kind marbling composition. The purpose of the research was to generate advanced meat constructions that actually replicate the structure, texture, and characteristics of specific meats, in buy to tackle the different limitations of current cultured meat creation methods.
The researchers imagine their work could also support to handle the world-wide improve in food desire, as well as mitigate the influence of contributing elements such as local climate adjust, deforestation and ozone depletion.
“The technology from this study was made to replicate the advanced and gorgeous marble framework viewed in Japan’s entire world-renowned Wagyu beef,” stated Professor Michiya Matsusaki of Osaka University. “We hope that cultured Wagyu steak meat will become a new sector for Japan.”
Solving the ‘protein crisis’
With the world’s populace envisioned to exceed 9.7 billion by 2050, the subsequent boost in food need, alongside the effect of local climate alter, suggests it may possibly not be probable to deliver a enough provide of meals. As such, the scientists consider the environment could be faced with a so-identified as ‘protein crisis’, prompting higher fascination in plant-dependent protein and cultured meat as substitute protein resources.
Study into cultured meat has been underway for some time, and 3D printing is actively playing an rising part in aiding not only the exploration in this region, but also the professional manufacturing of cultured meat items.
For occasion, 3D printed food items start off-up Redefine Meat a short while ago introduced its initial sequence of 3D printed ‘New-Meat’ goods to chosen places to eat and lodges in Israel, with the rollout prepared to prolong to Europe later this 12 months, and to the US and Asia in 2022. In the meantime, fellow food printing get started-up SavorEat has teamed up with worldwide hospitality agency Sodexo to pilot its Robot Chef 3D printing technologies and 1st alt-meat products at US universities future 12 months.
Elsewhere, meals tech organization MeaTech has declared options to enter chicken excess fat production throughout 2022 using the technologies acquired from its acquisition of Peace of Meat, a developer of cultured fats products, past calendar year.
3D printing Wagyu beef
The Osaka University and Toppan researchers sought to strengthen the framework of 3D printed meat, which they say has so far struggled to adequately replicate the texture and layers of genuine meat. Current analysis into 3D printed meat has developed constructions consisting only of muscle mass fiber, they claim, providing it a mince-meat construction that fails to properly recreate the distinct features of individual meats.
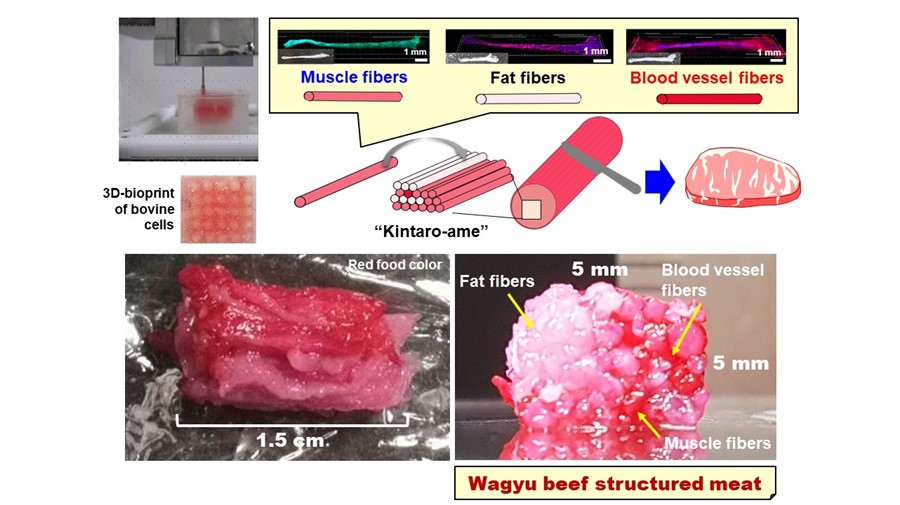
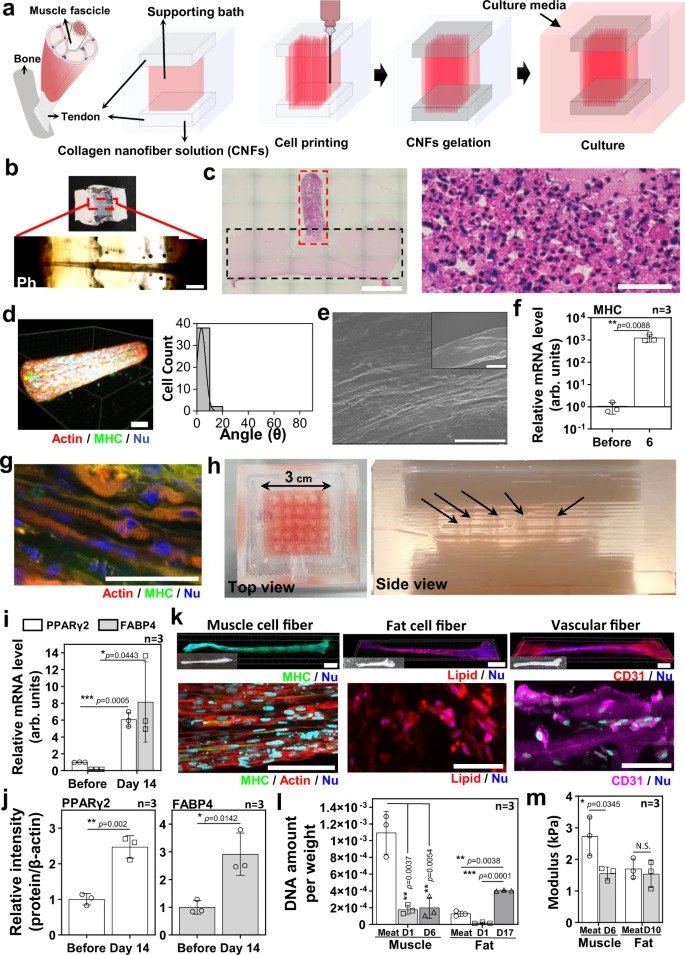
To handle this, the crew created an original tissue modeling technologies that employed 3D bioprinting to produce tendon-like gels that could be assembled to fabricate a steak-like meat structure that was 10 mm prolonged and 5 mm wide. The researchers’ technology, named tendon-gel-built-in bioprinting (Idea), enabled the fabrication of meat buildings with different tissue make-ups, in buy to additional precisely replicate their real meat equivalents.
“To allow us to use 3D printing engineering to stably create muscle mass, excess fat, and blood vessel tissue, it was important to suppress the contraction that occurs in the course of differentiation induction,” reported Matsusaki. “Focusing on the actuality that tendons help muscle tissues in the overall body, we as a result produced ‘artificial tendon tissue’ using sort I collagen, the main constituent of tendons. By then attaching just about every fibrous tissue to the artificial tendon tissue, it has come to be feasible to stably generate the fibrous tissues for creation.”
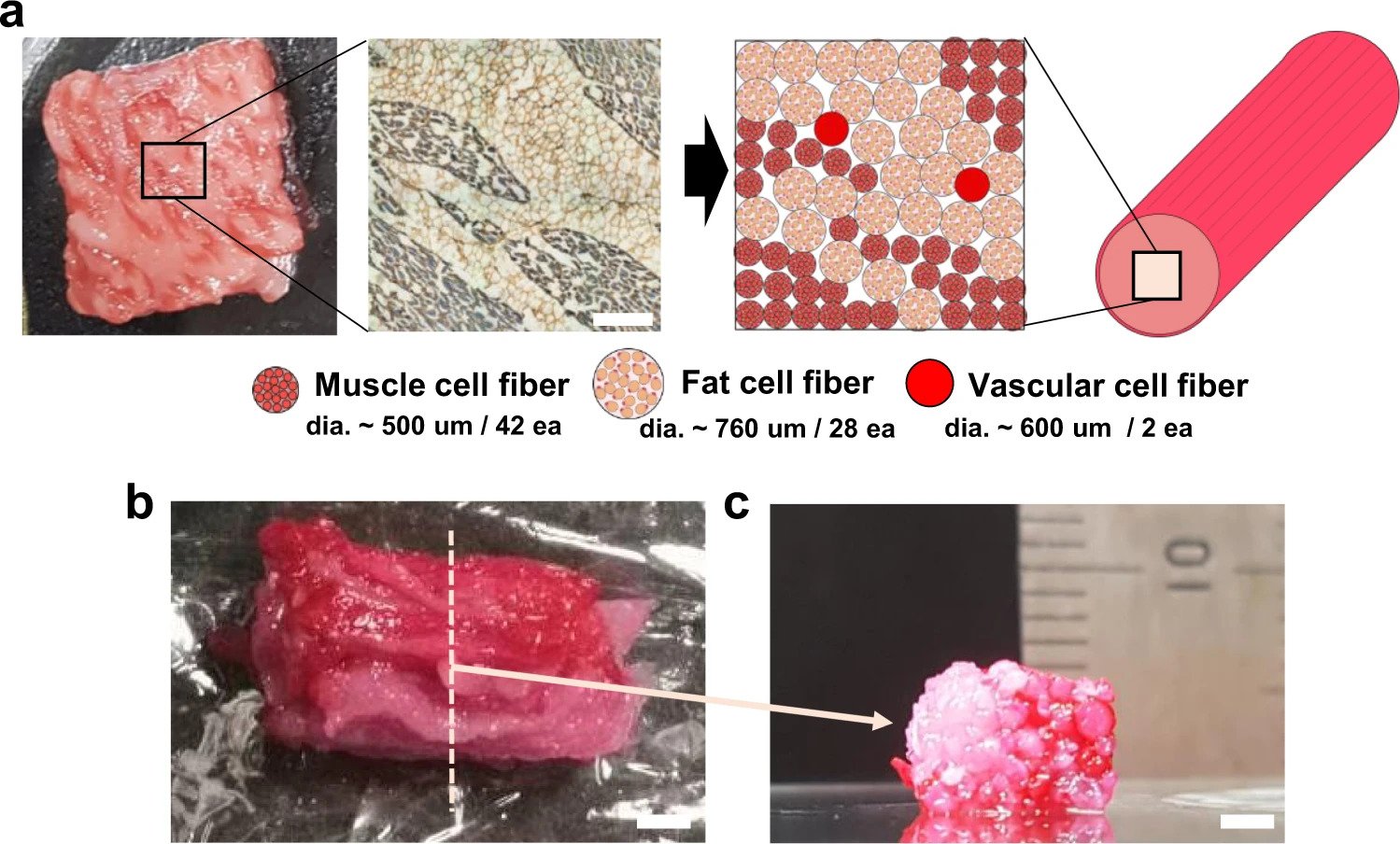
To precisely reproduce industrial Wagyu beef, the scientists took a cross-sectional graphic of a Wagyu lower to make a model pattern that confirmed the required selection of muscle, unwanted fat, and blood capillary mobile fibers needed, as properly as their arrangement. The mobile fibers have been received by using the Idea method and were then stacked in line with the design image, just before becoming handled with transglutaminase, a typical foodstuff cross-linking enzyme, to accelerate the assembly procedure.
The Wagyu beef composition was constructed from a overall of 72 3D printed bovine mobile fibers, which includes 42 muscle mass fibers, 28 adipose tissues, and two blood capillaries.
As the ratio of muscle, adipose tissues, and blood capillaries change concerning diverse meat kinds, the researchers’ engineering allows the various varieties of fibers to be 3D printed accordingly to correctly replicate their particular person constructions. For instance, Wagyu rump is built up of 10.7 p.c adipose tissues, whereas Wagyu sirloin contains 47.5 percent adipose tissues, which will have a considerable impression on the texture and construction of both cuts.
Increasing cultured meat generation
In accordance to the researchers, further more enhancement of their technological innovation will not only make it probable to generate sophisticated meat structures that replicate the individual characteristics of distinct meat forms and cuts, but also to control the fat and muscle information of cultured meat. Automated devices for features of the approach other than 3D printing, these types of as cultivation, could also make it possible to create cultured meat in any area.
As this kind of, the scientists consider their technologies could assist to deal with the United Nations’ (UN) Sustainable Growth Ambitions (SDGs) about environment preservations and resolving food stuff crises. The investigation could also perhaps aid to negate the environmental destruction resulting from deforestation for the output of cereal grains desired for livestock farming, as perfectly as ozone depletion triggered by the CO2 emanating from livestock.
Also, manufacturing cultured meat on-demand and in any area could have an strength-conserving outcome, as it can be established far quicker than the time it normally takes to grow cattle for slaughter.
Additional details on the review can be found in the paper titled: “Engineered total slash meat-like tissue by the assembly of mobile fibers working with tendon-gel integrated bioprinting,” released in the Mother nature Communications journal. The examine is co-authored by D. Kang, F. Louis, H. Liu, H. Shimoda, Y. Nishiyama, H. Nozawa, M. Kakitani, D. Takagi, D. Kasa, E. Nagamori, S. Irie, S. Kitano, and M. Matsusaki.
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter for the most recent news in additive producing. You can also keep related by next us on Twitter and liking us on Fb.
Looking for a occupation in additive production? Visit 3D Printing Work for a collection of roles in the sector.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel for the hottest 3D printing video shorts, opinions and webinar replays.
Featured image reveals the production course of action and samples of cultured Wagyu beef produced working with the 3D printing-based mostly initial tissue modeling technology. Image by way of Toppan.




More Stories
Negotiating Technology Contracts
Civilian Applications of GPS Technology
Technology and the Age of Exploration